STATIC CODE ANALYSIS
INTRODUCTION
Establishing standards and security in application code development is fundamental for ensuring that software remains secure, manageable, and aligned with organizational goals.
Enhanced Security
- Structured and standards-compliant code mitigates security risks by adhering to best practices that reduce vulnerabilities.
Operational Efficiency and Maintainability
- Consistency in code structure ensures that it is understandable and accessible between team members.
- A well-organized codebase reduces onboarding time for new developers, accelerates troubleshooting and updates, and prevents disruptions caused by unclear or disjointed code.
Optimized Performance and Scalability
- Adherence to best practices in coding standards enables applications to perform optimally under varying workloads.
- Scalability is crucial for long-term sustainability and supports business growth by enabling the application to handle increased user demand and feature expansion seamlessly.
Regulatory and Compliance Assurance
- In many sectors, regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS) requires strict adherence to coding and security standards.
- Following these standards in the code ensures that the application meets necessary regulatory guidelines, thereby avoiding potential fines and legal liabilities.
- Compliance-ready code also simplifies audit processes and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to data protection and ethical software practices.
Reduced Technical Debt and Long-Term Cost Savings
- Unstructured code often results in technical debt, requiring extensive resources to refactor, update, or maintain.
- By implementing standards from the outset, organizations minimize technical debt, making the code more resilient and adaptable to change.
Increased Quality and Reliability
- A codebase developed with standardized practices promotes reliability, allowing the software to function predictably across various environments and conditions.
- This builds user confidence in the product and enhances the organization’s reputation for delivering dependable, high-quality software solutions.
SAST
SAST - Static Application Security Testing
- It is a security practice used to analyze and identify vulnerabilities within an application’s source code, bytecode, or binary without executing the program.
-
SAST tools examine the application at an early stage in the development lifecycle (typically during the coding or building phase) to find potential security weaknesses.
Key Aspects of SAST
Early Detection of VulnerabilitiesComprehensive Code CoverageAutomated TestingCode Standards and Compliance
Benefits of SAST
Early Remediation: By identifying issues during the coding phase, SAST allows developers to resolve vulnerabilities promptly, reducing the likelihood of introducing new security flaws.Reduced Costs: Fixing vulnerabilities early in development is significantly less costly than addressing them post-release.Improved Security Awareness: SAST tools often provide detailed reports and remediation guidance, helping developers to improve their security knowledge and write more secure code.
SONARQUBE
SonarSourcethe company developedSonarQube.Open-sourceplatform designed for continuous inspection of code quality.-
Tools to analyze their code for various aspects, including bugs, code smells, vulnerabilities, and code coverage.
Features of SonarQube
- Static Code Analysis
- Multi-Language Support
- Code Quality Metrics
- Customizable Rules and Profiles
- Integration with CI/CD
Static Analysis
-
As a SAST tool, SonarQube analyzes the codebase without executing the application, focusing on identifying vulnerabilities and quality issues in the source code.
-
This is essential for early detection of security flaws.
Vulnerability Detection
-
SonarQube includes security rule sets that align with industry standards (such as OWASP Top Ten).
-
Enabling teams to detect and address potential vulnerabilities.
Code Quality Improvement
- By highlighting code smells and potential bugs, SonarQube aids in enhancing overall code quality and maintainability, which are critical for secure software development.
SonarQube Setup Using Docker
Architecture Diagram
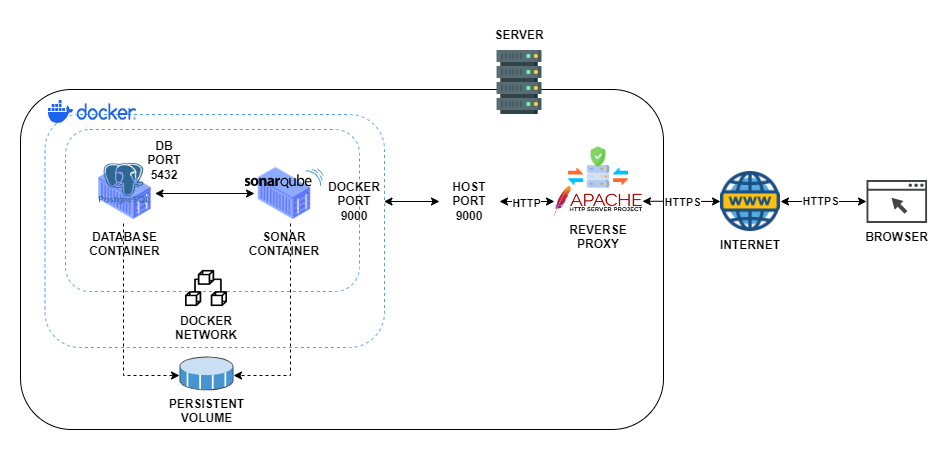
DOCKER
- Docker is a tool that makes it easy to create, deploy, and run applications in lightweight, portable containers, allowing software to run the same way across different environments.
DOCKER IMAGE
- Docker image is a lightweight, standalone package that includes everything needed to run a piece of software, such as code, libraries, and dependencies.
SonarQube Scan
-
A Sonar scan (or SonarQube scan) is the process of analyzing source code with SonarQube to assess code quality and identify potential issues.
Code Quality- Identifying and classifying issues based on severity, such as code smells
(suboptimal practices), bugs, and vulnerabilities.
Security Vulnerabilities- Checking for known security weaknesses, such as injection flaws, access control issues, and insecure code practices.
Maintainability- Evaluating code for readability, complexity, and adherence to best practices to ensure the code is maintainable and less prone to errors.
Duplicated Code Detection- Highlighting repeated code patterns to encourage reusability and reduce maintenance overhead.
Code Coverage- Integrating with test coverage tools to show how much of the codebase is covered by tests, which indicates the reliability of the code.
- Identifying and classifying issues based on severity, such as code smells
SonarQube Scanning Process
Static Code Analysis
- SonarQube performs static analysis without running the code.
- It parses the source files and checks against its extensive rules database.
Plugins and Rulesets
- The scan uses predefined rules based on the programming language, framework, or specific security standards
(like OWASP or CWE).
Reporting
- After a scan, SonarQube provides a dashboard view with issues categorized by severity, along with suggested fixes and quality gate status to indicate if the project meets defined quality thresholds.
Ways to Run a Sonar Scan
SonarQube Scanner
- The command-line tool specifically designed to trigger scans.
SonarQube Plugins
- IDE plugins
(like SonarLint)provide feedback in real-time as developers code.
CI/CD Integration
- SonarQube can integrate with CI/CD pipelines
(such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions)to automatically scan code upon each commit or pull request.
Custom CI/CD With GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions
-
GitHub Actions is a tool for automating tasks in your GitHub projects.
-
It allows to write custom workflows or use pre-built ones, and it’s fully integrated into GitHub, making it easy to manage all automation in one place.
-
GitHub Actions can automate code quality checks as part in pipeline.
GitHub Actions Pipeline Architecture
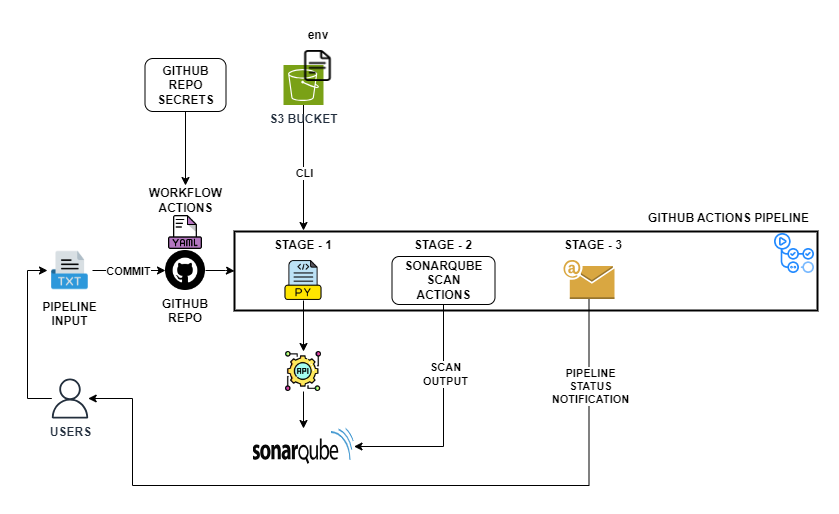
From the above architecture, the setup remains central for all projects.
Code from different code repository can be scanned from this central repository.
GitHub Secrets
GitHub TokensAWS Access KeysS3 Bucket DetailsSMTP Creds
were stored in central pipeline repository secrets.
WorkFlow
- A workflow is an automated process that runs specific tasks based on triggers, such as pushing code, creating a pull request, or scheduling a run.
- Workflows are defined in YAML files within your repository under
.github/workflows/. -
Each workflow file describes the sequence of steps and conditions for automation tasks, like building, testing, or deploying code.
Key Points About Workflows
Triggers- Specify when workflows run, like on push, pull_request, or on a schedule.
Jobs- Each workflow is made up of one or more jobs, which run tasks in sequence or parallel.
Steps- Jobs contain individual steps, which are specific actions or commands to perform.
Actions- Workflows can use reusable actions
(pre-built tasks)from GitHub’s marketplace or custom commands.
Pipeline Process
Pipeline has three different stage or jobs.
Stage - 1
- Creating project in SonrQube dashboard.
Stage - 2
- Run sonar scan against the target application source code and send the results to SonarQube.
Stage - 3
- Send email notification to user.
